1. Introduction
Solar power is becoming more popular as people look for ways to save money on electricity bills and reduce their impact on the environment. But did you know that there are different types of solar power systems?
Not all solar systems work the same way. Some are connected to the electricity grid, while others work completely on their own. Some can store energy in batteries, while others send extra electricity back to the grid.
In this article, we’ll explain the three main types of solar power systems in simple terms:
- On-grid solar system (also called grid-tied system)
- Off-grid solar system (stand-alone system)
- Hybrid solar system (solar with battery storage and grid connection)
We’ll also break down the key components of a solar system and how they work together.
2. Types of Solar Power Systems
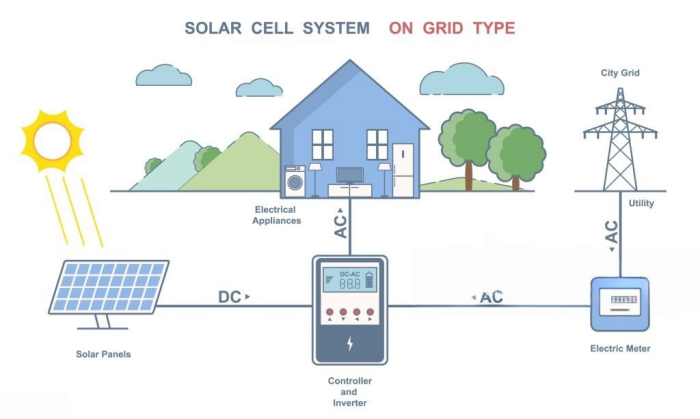
2.1 On-Grid Solar System (Grid-Tie System)
An on-grid solar system is the most common type of solar system. It is connected to the public electricity grid, meaning you can still use power from the grid when needed.
How It Works:
- Solar panels generate electricity during the day.
- The electricity is used in your home, and any extra power is sent to the grid.
- If your solar panels don’t produce enough electricity (like at night), you get power from the grid.
Benefits of On-Grid Systems:
✅ No need for expensive battery storage.
✅ You can earn money or credits for the extra electricity you send to the grid (Feed-in Tariff).
✅ It’s cheaper and easier to install than other systems.
Limitations:
❌ Does NOT work during a power outage (blackout) for safety reasons.
❌ You are still dependent on the electricity grid.
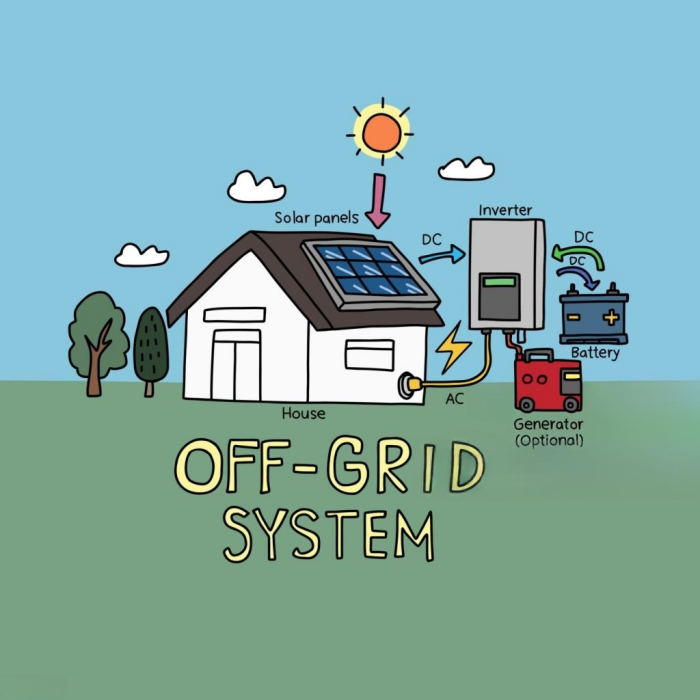
2.2 Off-Grid Solar System (Stand-Alone System)
An off-grid solar system is completely independent from the electricity grid. It relies on solar panels and batteries to provide power, even at night or during cloudy days.
How It Works:
- Solar panels generate electricity and charge batteries during the day.
- At night or when it’s cloudy, the batteries provide stored power.
- If the battery runs low, a backup generator is usually needed.
Benefits of Off-Grid Systems:
✅ Perfect for remote areas with no access to the electricity grid.
✅ Full energy independence—no electricity bills!
✅ Works even during blackouts.
Limitations:
❌ Batteries are expensive and need regular maintenance.
❌ A backup generator is often required for long cloudy periods.
❌ Requires careful planning to ensure enough power year-round.
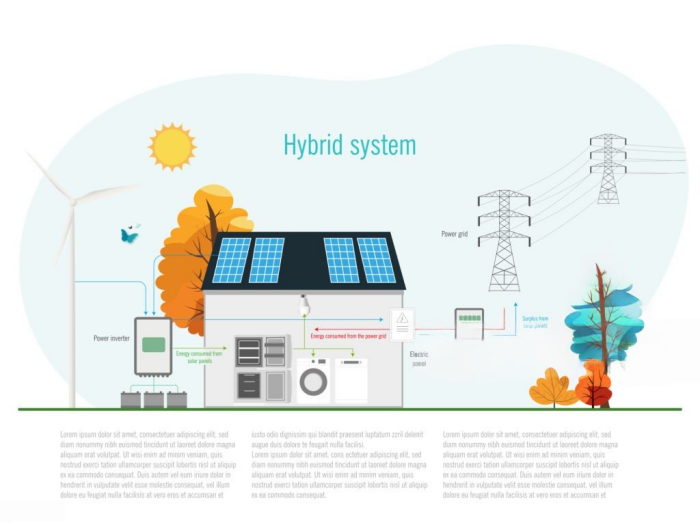
2.3 Hybrid Solar System (Solar with Battery & Grid Connection)
A hybrid solar system combines the benefits of both on-grid and off-grid systems. It is connected to the electricity grid but also has a battery storage system.
How It Works:
- Solar panels generate electricity and supply power to your home.
- Any extra electricity charges the batteries instead of going directly to the grid.
- At night or during blackouts, the batteries provide power.
- If the batteries are empty, you can still use electricity from the grid.
Benefits of Hybrid Systems:
✅ Provides backup power during blackouts.
✅ Reduces electricity bills by storing and using solar power efficiently.
✅ Can sell extra electricity to the grid (depending on your setup).
Limitations:
❌ Batteries add extra costs to the system.
❌ More complex installation compared to on-grid systems.
3. Solar System Components and How They Work
All solar power systems, whether on-grid, off-grid, or hybrid, have similar components. Let’s take a look at how they work.
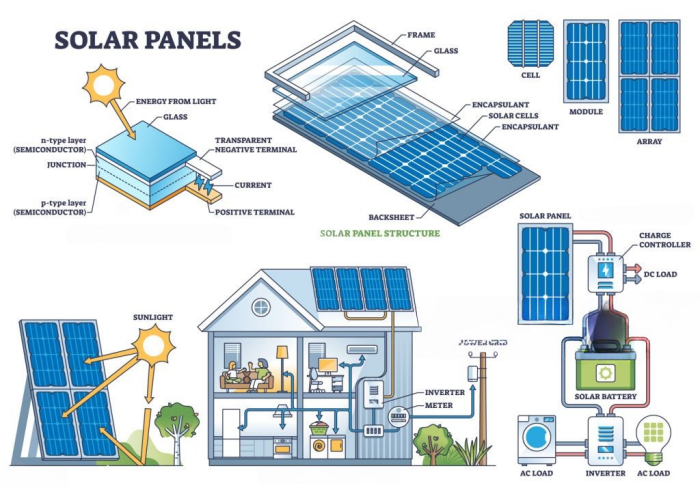
3.1 Solar Panels
Solar panels are made of photovoltaic (PV) cells that convert sunlight into electricity.
- They produce direct current (DC) electricity when exposed to sunlight.
- More panels mean more electricity.
- The amount of power they generate depends on sunlight intensity, panel quality, and weather conditions.
Important Note: Solar panels generate electricity from light energy, not heat. This means they can work even on cold days as long as there is sunlight.
3.2 Solar Inverter
Solar panels produce DC electricity, but homes and businesses use AC electricity. This is where the solar inverter comes in.
- The inverter converts DC electricity into AC electricity for home use.
- In an on-grid or hybrid system, the inverter also manages the flow of electricity between the home, batteries, and grid.
Some systems use micro-inverters, which are attached to individual solar panels instead of using one big central inverter.
3.3 Distribution Board
Once the inverter converts electricity to AC, it is sent to the distribution board.
- This board directs electricity to different appliances in the house.
- If there is excess electricity, it either charges batteries (in off-grid or hybrid systems) or goes to the grid (in on-grid systems).
3.4 Solar Batteries
Solar batteries store excess electricity so that it can be used later.
- Lead-acid, AGM, gel, and lithium are common battery types.
- Lithium batteries are the most efficient and long-lasting but are also the most expensive.
- Used in off-grid and hybrid systems to provide power at night and during blackouts.
4. On-Grid Solar System in Detail
✅ Most affordable and easiest to install
✅ Saves money on electricity bills
✅ Can sell extra power to the grid
❌ Does not work during blackouts
❌ Still dependent on the electricity grid
5. Off-Grid Solar System in Detail
✅ Full energy independence
✅ No electricity bills
✅ Works in remote locations
❌ Expensive batteries and backup generator needed
❌ Must be carefully designed to work in all seasons
6. Hybrid Solar System in Detail
✅ Best of both worlds—battery backup and grid connection
✅ Works during blackouts
✅ Can save and sell excess power
❌ Higher initial cost due to battery storage
❌ More complex setup compared to on-grid systems
7. Conclusion
Solar power systems are a great way to reduce electricity bills and be more environmentally friendly. However, choosing the right type of system depends on your energy needs and budget.
- If you want a simple and affordable system, on-grid solar is the best choice.
- If you live in a remote area without grid access, off-grid solar is your only option.
- If you want backup power during blackouts and more control over your electricity, a hybrid solar system is the way to go.
Investing in solar energy is a smart decision for the future. By understanding how these systems work, you can choose the one that fits your lifestyle best.
FAQs
1. Can I install solar panels without batteries?
Yes! If you choose an on-grid solar system, you don’t need batteries.
2. Do solar panels work on cloudy days?
Yes, but they produce less electricity because there is less sunlight.
3. How long do solar batteries last?
Most batteries last 5-15 years, depending on the type and usage.
4. Can I use a hybrid system without a battery?
Yes, but adding a battery helps store excess energy for later use.
5. What happens if my battery is full?
In a hybrid system, extra power can be sent to the grid. In an off-grid system, power production stops when the battery is full.
Post time: Mar-05-2025